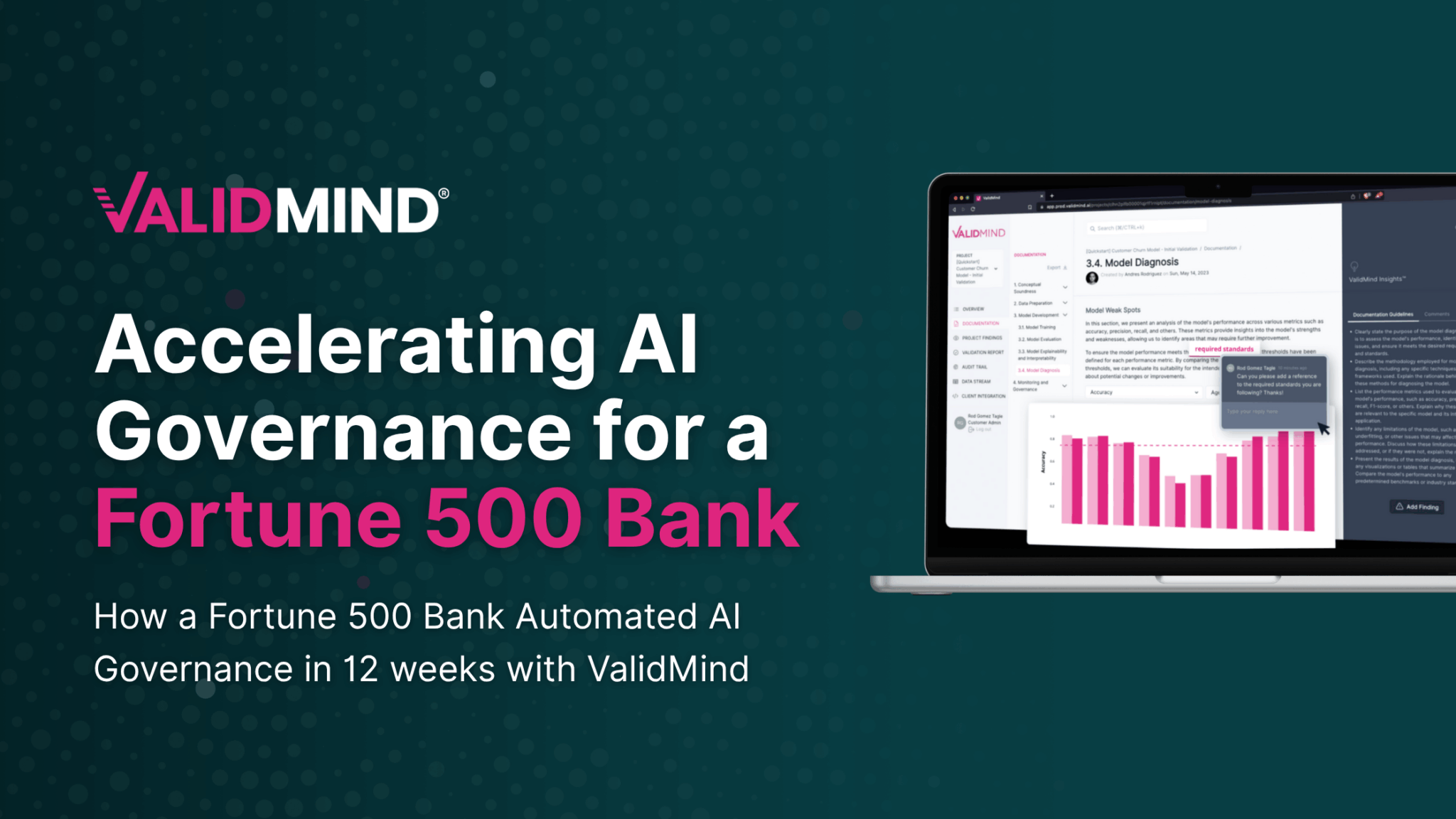
Navigating SS1/23: A Compliance Guide for Model Risk Management (MRM) Teams
Issued in 2023 by the U.K.’s Prudential Regulation Authority (PRA), SS1/23 is the first supervisory statement dedicated to model risk management (MRM). Its objective is to elevate MRM practices among banks and insurers, with a strong emphasis on board-level accountability and integration into broader risk frameworks. Not only does SS1/23 align with the U.S. Federal Reserve’s SR 11-7, it reflects the PRA’s expectation for U.K. institutions by requiring them to embed MRM into their organization’s entire risk management.
This regulation is becoming more and more relevant as financial institutions are starting to rely heavily on AI, machine learning, large language models, and generative AI. The PRA has highlighted that these models introduce new risks that MRM teams must address, including aspects like explainability, data provenance, fairness, and accountability.
Complying with SS1/23: Elevating Model Risk to a Major Priority
SS1/23 places model risk on par with credit and market risk, requiring it to be fully integrated into banks’ overall risk management frameworks. To meet this standard, leadership must strengthen their focus on MRM, as flawed models can damage a bank’s reputation and financial durability.
The framework minimizes risks through four PRA principles: model governance, model inventory and documentation, model development and validation, and ongoing risk assessments. Governance is the foundation that turns these expectations into accountability. Strong oversight embeds MRM into daily operations and guarantees that model use aligns with the bank’s risk appetite.
The PRA expects senior management to have the expertise needed to challenge assumptions and decisions, including those made by AI models. It also stresses the need for independent validation and scrutiny, where model developers and users can be openly questioned by separate oversight functions.
To prevent failure, banks should implement governance structures that support and hold MRM teams accountable. This oversight ensures policies are applied consistently and sets a standard across the institution.
Model Inventory and Documentation
A robust model inventory and documentation framework provides banks with the transparency needed to manage model risk effectively. Under SS1/23, firms must maintain a detailed inventory of all models, classifying each by complexity so that high-risk models receive stricter monitoring, documentation, and validation than lower-risk ones. Comprehensive documentation creates a clear audit trail and enables senior management and boards to oversee model use with confidence. Keeping records up to date further strengthens transparency and supports consistent communication across the institution.
Model Development and Validation: Challenging Models Before and After Deployment
SS1/23 expects banks to design models that are robust and tested before and after deployment, with development providing the foundation for accuracy and validation serving as the independent check that ensures models perform as intended under real-world conditions.
Firms must maintain a process that tests models throughout their lifecycle with human oversight to confirm recommendations are being acted upon. For AI driven models, validation extends beyond accuracy metrics and includes testing for data transparency, bias, and fairness. Embedding these lifecycle standards will allow banks to adapt to rapid technological change while keeping models relevant and dependable.
Watch our Webinar Replay to learn more about SS1/23: How to Navigate PRA’s SS1/23 Regulation
Risk Assessment: Mitigating Weaknesses and Third-Party Risks
Left unchecked, models can quickly become a source of instability. Errors in development or lapses in validation may lead to flawed outputs and financial losses. SS1/23 makes clear that risk mitigation must be continuous.
Effective risk assessment means stress testing assumptions and installing safeguards before vulnerabilities disrupt operations. This is where third-party oversight comes in. When external models or services are used, firms must have contracts and controls in place guaranteeing room for transparency and independent challenge. The PRA also expects firms to be inspection ready, with documented evidence of model decisions, changes, and validation outcomes.
As technology evolves, models must be updated and revalidated to reflect new data and methods. Risk assessment serves as the feedback loop that ties together governance, documentation, and validation, ensuring consistency across the institution.
Applying SS1/23 to Modern Risks
Complying with SS1/23 is important for regulatory alignment and maintaining adaptability as banks adopt AI and GenAI. The PRA expects firms to embed explainability, fairness, and accountability into their model risk practices, ensuring that boards and senior management can provide effective oversight in a fast changing environment.
By strengthening governance, inventories, documentation, development, validation, and ongoing risk assessments, banks can put SS1/23’s principles into practice. Together, these measures build the transparency, accountability, and adaptability needed to manage the risks of modern AI-driven systems while enabling innovation responsibly.
Want to learn more about SS1/23? Download our technical brief today.